01 The necessity of garbage incineration
As human beings continue to use natural resources to create a material civilization, a large amount of garbage is also generated.
According to the prediction of the United Nations Environment Program, with the development of the world economy, the global middle-class population will rise substantially. By 2025, the amount of global urban waste will increase from the current annual 1.3 billion tons to 2.2 billion tons. In this situation, we cannot be limited to the passive “defense” methods of landfilling and composting, but should actively take effective measures to carry out comprehensive and scientific treatment of garbage. Waste incineration power generation is the current ideal choice.
As a widely adopted urban domestic waste treatment method in developed countries, the incineration system complies with the three principles of "harmlessness, reduction, and recycling".
Reduction: After the waste is incinerated, the general volume can be reduced by more than 90% and the weight by more than 80%. Landfilling after garbage incineration can effectively reduce the occupation of land resources.
Harmless: After high-temperature incineration, it can eliminate a large number of harmful bacteria and toxic substances in the garbage, and can effectively control secondary pollution.
Large amounts of household waste are burned in the open air and spontaneous combustion of landfills emits dioxin into the atmosphere, which is several thousand times that of the same amount of waste discharged by modern incineration. Research from Germany shows that when garbage is transported to an incineration plant, the dioxin unit content has reached 50 ng. After domestic waste is incinerated, the original dioxin in the garbage is decomposed, and the dioxin discharged into the air is equivalent to 1% of the original content.
Recycling: The thermal energy generated after garbage incineration can be used for power generation and heating to achieve the comprehensive utilization of resources. Waste-to-energy can not only turn waste into treasure, produce electrical energy, but also save coal resources.
Internationally, it is generally believed that the average low calorific value of garbage can reach 3000 kcal/kg, the calorific value of standard coal is 7000 kcal/kg, and burning 2.3 tons of garbage can save 1 ton of coal. China ’s urban garbage is mainly domestic garbage, with large water content and a calorific value of only 1,000 kcal/kg, but even so, burning 7 tons of garbage can save 1 ton of coal, even if half of the city ’s garbage is used for incineration throughout the year, It can save more than 20 million tons of coal.
02 Technical principles of waste incineration power generation
Environmental equipment factory is to collect all kinds of waste and sort it. Among them: First, high-temperature incineration (completely eliminating pathogenic organisms and corrosive organic matter) with high combustion value, the heat energy generated during high-temperature incineration (the generated smoke is treated) is converted into high-temperature steam, and the turbine is rotated Make the generator produce electrical energy. The second is the fermentation, anaerobic treatment of the incombustible organic matter, and finally drying and desulfurization to produce a gas called methane (biogas), which is then converted into steam by combustion, which drives the turbine to rotate and drives the generator to generate electrical energy.
The garbage is transported to the incineration plant by the transport truck, weighed by the weighbridge, then opened to the discharge door and discharged to the garbage pond. The garbage crane sends the garbage into the feed hopper and into the furnace, where it is burned in the incinerator. The inlet of the blower is connected to the garbage pond, and the odor of garbage can be sent to an incinerator with a combustion temperature of about 850 to 1100 ° C for thermal decomposition to become odorless gas.
The garbage goes through three stages of drying, burning, and burning, and the garbage is fully burned at a high temperature of 850-1100 degrees. Through the DCS automatic control system and automatic combustion control system, the combustion conditions of garbage in the furnace can be monitored and adjusted in real-time, and the operating speed of the grate and the amount of combustion air can be adjusted in time. The burning flame and the high-temperature flue gas generated by garbage incineration generate high-temperature steam through a natural circulation boiler, which provides a steam source for the steam turbine generator set.

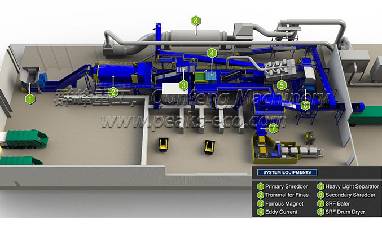
Waste to Energy (Incineration)
Waste incineration power generation treatment process
The main technologies of the main device of the incineration system include five types of technologies, including mechanical grate incinerators, fluidized bed incinerators, rotary incinerators, CAO incinerators, and pulse-throw incinerators. environmental equipment factory to introduce you:
1. Mechanical grate incinerator
Working principle: The garbage enters the inclined downward grate through the feed hopper (the grate is divided into a drying area, a combustion area, and a burn-out area). Due to the interlaced movement between the grate, the garbage is pushed down and the garbage passes through in turn Various areas on the grate (when garbage enters from one area to another, it acts as a large turn) until it is burned out of the furnace.
The combustion air enters from the lower part of the grate and mixes with the garbage; the high-temperature flue gas generates hot steam through the heated surface of the boiler, and the flue gas is also cooled. Finally, the flue gas is discharged after being processed by the flue gas treatment device.
Features: The grate furnace domestic garbage incineration technology is stable in operation, has a strong ability to treat garbage thoroughly, and is suitable for continuous operation. After optimized flue gas treatment technology, the emission reaches the standard.
However, the material requirements and processing accuracy requirements of the grate are high, requiring that the contact surface between the grate and the grate is relatively smooth, and the gap between the rows is relatively small. In addition, the mechanical structure is complex, the damage rate is high, and the amount of maintenance is large.
2. Fluidized bed incinerator
Working principle: The furnace body is composed of a porous distribution plate. A large amount of quartz sand is added into the furnace chamber, the quartz sand is heated to above 600 ℃, and hot air above 200 ℃ is blown into the bottom of the furnace to make the hot sand boil, and then put in Rubbish.
Rubbish boils with hot sand, and the rubbish is quickly dried, caught on fire, and burned. The proportion of unburned garbage is lighter and continues to boil. The proportion of burned garbage falls to the bottom of the furnace. After water cooling, the coarse and fine slag are sent to the outside of the plant with a sorting equipment. A small amount of medium slag and The quartz sand is sent back to the furnace through the lifting equipment to continue to use.
Features: The fluidized bed is fully combusted and the combustion control in the furnace is good, but the amount of dust in the flue gas is large, the operation is complicated, the operating cost is high, the uniformity of the fuel particle size is high, and a high-power crushing device is required. The equipment is badly worn and the equipment maintenance is heavy. It is easy to cause coking, and the system's continuous operation ability is low.
3. Rotary incinerator
Working principle: The rotary incinerator is arranged with cooling water pipes or refractory materials along the furnace body, and the furnace body is placed horizontally and slightly inclined. Through the non-stop operation of the furnace body, the garbage in the furnace body is fully burned, and at the same time, it moves in the inclined direction of the furnace body until it is burned out and discharged from the furnace body.
Features: High equipment utilization, low carbon content in ash, low excess air, and low harmful gas emissions. But the combustion is not easy to control, and it is difficult to burn when the calorific value of garbage is low.
4. CAO incinerator
Working principle: The garbage is transported to the storage tank, enters the biochemical treatment tank, and dehydrated under the action of microorganisms, so that natural organic matter (kitchen waste, leaves, grass automatic garbage power generation crane, automatic garbage power generation crane, etc.) is decomposed into powder, other solids Synthetic organic matter including plastics and rubber and inorganic matter in the garbage cannot be decomposed and pulverized.
After screening, the unpulverized waste enters the first combustion chamber (temperature is 600 ℃) before entering the incinerator, and the combustible gas produced enters the second combustion chamber. The non-combustible and non-pyrolyzable components appear as ash The shape is discharged in the first combustion chamber.
The temperature in the second chamber is controlled at 860 ° C for combustion, and high-temperature flue gas heats the boiler to produce steam. The flue gas is discharged from the chimney to the atmosphere after treatment. The metal glass will not be oxidized or melted in the first combustion chamber and can be sorted and recovered in the ash.
Features: Recyclable useful materials in the garbage; but the processing capacity of a single incinerator is small and the processing time is long. At present, the daily processing capacity of a single furnace is up to 150 tons. Because the residence time of flue gas above 850 ℃ is difficult to exceed 1 second The clock is short, and the content of dioxins in the smoke is high, making it difficult to meet the environmental protection standards.
5. Pulse toss
Working principle: The garbage is sent to the drying bed of the incinerator through an automatic feeding unit for drying, and then sent to the first-stage grate. After high-temperature volatilization and cracking on the grate, the grate is thrown by the impulse aerodynamic device The garbage is thrown into the next level grate step by step, at this time the polymer material is cracked and other materials are burned.
In this way, it will enter the ash slag pool after being burned out at the end, and be discharged by the automatic slag removal device. Combustion-supporting air is injected into the air holes on the grate and mixed with the garbage to burn while suspending the garbage in the air. The volatilized and cracked substances enter the second-stage combustion chamber for further cracking and combustion. The unburned flue gas enters the third-stage combustion chamber for complete combustion; the high-temperature flue gas heats the steam through the boiler heating surface, and the flue gas passes Discharge after cooling.
The advantages are:
(1) A wide range of waste disposal, capable of processing industrial waste, domestic waste, hospital waste, waste rubber tires, etc .;
(2) The combustion thermal efficiency is high, the normal combustion thermal efficiency is more than 80%, even if the domestic waste with large water content, the combustion thermal efficiency is more than 70%;
(3) Low operation and maintenance costs, due to the use of many special designs and a high level of automation control, there are few operating personnel (only two people are required for a furnace including ash removal personnel), and the maintenance workload is also small (4) High reliability, after nearly 20 years of operation, the failure rate of this incinerator is very low, the annual operation is more than 8000 hours, and the general utilization rate can reach more than 95%;
(5) The level of emission control is high. Due to the use of secondary flue gas burning and advanced flue gas treatment equipment, the flue gas is fully treated;
(6) The grate is purged by compressed air and has a self-cleaning function.
Environmental Equipment Factory
04 Requirements for discharge and treatment of pollutants from waste incineration power generation
1. Engineering Technical Requirements
The annual operating time of each incineration production line should be more than 8000 hours, and the design service period of the incineration system should not be less than 20 years.
The effective volume of the garbage pond shall be determined according to the rated garbage incineration volume for 5 to 7 days. Garbage ponds should be equipped with garbage leachate collection facilities. Domestic garbage storage facilities and leachate collection facilities should adopt closed negative pressure measures and ensure that they are under negative pressure during the operation period and furnace shutdown period. The gas in these facilities should be preferentially passed into incinerators for high-temperature treatment or collected and discharged after meeting the requirements of the "Standard Pollutant Discharge Standard" through deodorization treatment.
The waste to energy system should ensure that the garbage is fully burned in the incinerator. The flue gas in the secondary combustion chamber should be kept at a temperature of not less than 850 ℃ for not less than 2 seconds. The incinerator slag heat reduction The rate should be controlled within 5%.
The waste incineration line must be equipped with a flue gas purification system, and it should be arranged in a unit system. The choice of the flue gas purification process should fully consider the changes in the characteristics of garbage and the number of incineration pollutants produced, as well as the impact of their physical and chemical properties, and pay attention to the matching between the combined processes.
Removal of acidic pollutants: acidic pollutants include hydrogen chloride, hydrogen fluoride, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, etc., and appropriate treatment processes should be used to remove them.
Measures should be taken to strictly control the emission of dioxins in the flue gas, including controlling the temperature, residence time and airflow disturbance conditions of the incineration flue gas in the combustion chamber; reducing the residence time of flue gas in the temperature range of 200 ℃ ~ 500 ℃; setting activated carbon Powder and other adsorbents are sprayed into the device.

Incineration System
2. Operational regulatory requirements
The amount of garbage stored in the garbage storage pond should be regularly monitored, and effective measures should be taken to discharge the leachate in the garbage storage pond. The leachate should be discharged after treatment.
On-line monitoring of the operating status of the incinerator should be achieved. The monitoring items should include at least the combustion temperature of the incinerator, the furnace pressure, the oxygen content of the flue gas outlet, and the carbon monoxide content. A sign should be set up in a prominent position to automatically display the main parameters and smoke of the operating conditions of the incinerator. Online monitoring data of major pollutants in the gas.
Automatic and continuous online monitoring of flue gas should be achieved. The monitoring items should include at least hydrogen chloride, carbon monoxide, soot, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, etc., and be connected to the local environmental sanitation and environmental protection authorities to achieve real-time data transmission.
Slag and fly ash generated by garbage incineration shall be properly handled or disposed of in accordance with regulations.
Effective odor control measures should be taken in each process, and the plant area should be free of obvious odors; deodorization systems should be used as required at relevant locations and maintained in a timely manner as required.
In garbage storage tanks, sewage and leachate collection tanks, underground buildings, production control rooms, and other places where biogas is easily collected, daily monitoring and supervision should be strengthened to ensure safe production.
3. Waste gas treatment requirements
The waste gas emitted by the waste incineration plant mainly comes from the flue gas generated by the incineration process. The main pollutants are dust, hydrogen chloride (HCl), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOX), carbon monoxide (CO), organic pollutants, Dioxins, and heavy metals.
The computer control system can achieve a high degree of automation of waste incineration, heat energy utilization, flue gas treatment, and other processes, control the set combustion conditions (such as furnace temperature is higher than 850 ℃, flue gas residence time is greater than 2 seconds, to maintain flue gas turbulent flow and Moderate peroxygen), so that the incineration system operates under rated conditions, the original emission concentration is reduced to a minimum, and to ensure the complete decomposition of organic substances such as dioxins.
Install a variety of effective flue gas treatment equipment, such as bag dust removal, activated carbon adsorption of harmful substances, etc., and use a flue gas online monitor-to continuously monitor the flue gas emission indicators of each incineration line to ensure the emission of flue gas pollutants from waste incineration plants Meet the required standards.
4. Odor control requirements
The compressed transport truck with good airtightness and automatic loading and unloading structure should be used to transport garbage to minimize odor overflow.
An air curtain should be installed at the entrance and exit of the garbage discharge hall, and the electric discharge door should be closed before and after the discharge of the garbage truck to prevent the odor from escaping.
The garbage pond should adopt a closed design, with an air suction port above the garbage pond to guide the malodorous gas as combustion air into the incinerator for high-temperature decomposition, and make the garbage pond and the discharge hall under negative pressure.
Spare activated carbon exhaust gas purification facilities should be set up. During the maintenance shutdown of the whole plant, the odor in the garbage pond must be purified by the activated carbon exhaust gas purification facilities before it can be discharged.
5. Dioxin emission control requirements
The so-called dioxin is actually an abbreviation for dioxin. It refers to the two major categories that contain many similar species or isomers with similar structure and properties. There are a total of 210 organic compounds, but only a few of them are Species are considered toxic.
Dioxin is not a unique public hazard in waste incineration plants. It is a compound produced by heating organic matter together with chlorine and is a relatively common chemical phenomenon. Dioxins can be found in the air, soil, water, food, and garbage. Studies have shown that food is its main source. About 90% of the dioxins in human contact come from the diet.
The waste incineration plant controls the emission of dioxin, mainly adopting the mature "3T" and high-efficiency purification technology. One is to maintain the temperature in the incinerator chamber above 850 degrees, and control the flue gas to stay in the furnace for more than 2 seconds so that It is completely decomposed; the second is that the flue gas passes through the most advanced purification treatment system to control the unit dioxin concentration within 0.1 (ng TEQ / m3), reaching the most stringent international emission standards.
6. Slag and fly ash control requirements
The slag is mainly the residue of household garbage after incineration, and its production depends on the composition of the garbage. Its main components are manganese oxide (MnO), silicon dioxide (SiO2), calcium oxide (CaO), and aluminum oxide (Al2O3), Iron oxide (Fe2O3), scrap metal, and a small amount of unburned organic matter.
After the slag generated by garbage incineration is treated at a high temperature and harmless, and then separated by magnetic separation, etc., the slag can be comprehensively used, and the part that cannot be comprehensively used can be sent to the sanitary landfill for landfill.
Each device of the fly ash collection, storage, and processing system should be kept in a closed state. When the flue gas purification system uses dry or semi-dry methods to remove acid gases, the fly ash treatment system should adopt mechanical or pneumatic ash removal methods; when using the wet method, the fly ash should be effectively separated from the sewage.
Fly ash is a hazardous waste and must be collected separately. It must not be mixed with domestic waste, incineration residues, etc., or mixed with other hazardous waste. Fly ash from incineration of garbage shall not be stored in the factory area for a long period of time, shall not be subjected to simple disposal, and shall not be transported out and discharged at will.






